| alphabet Apr 19th 2013, 00:29 | | | | Line 26: | Line 26: | | | #* '''2005''', Satinder Bal Gupta, ''Comprehensive Discrete Mathematics & Structures'', Laxmi Publications, page 237: | | #* '''2005''', Satinder Bal Gupta, ''Comprehensive Discrete Mathematics & Structures'', Laxmi Publications, page 237: | | | #*: There are 26 '''alphabets''' in English. | | #*: There are 26 '''alphabets''' in English. | | | + | # The simplest rudiments; elements. | | | + | #* Macaulay | | | + | #*: The very '''alphabet''' of our law. | | | | | | | | ====Derived terms==== | | ====Derived terms==== |
Latest revision as of 00:29, 19 April 2013 [edit] English [edit] Etymology From Late Latin alphabētum, from Ancient Greek ἀλφάβητος (alphabētos), from the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, alpha (Α) and beta (Β), from Phoenician aleph 𐤀 ("ox") and beth 𐤁 ("house"), so called because they were pictograms of those objects. [edit] Pronunciation - IPA: /ˈæl.fə.bɛt/, X-SAMPA: /"{l.f@.bEt/
- (uncommon:) IPA: /ˈæl.fə.bɪt/, X-SAMPA: /"{l.f@.bIt/
-
- Hyphenation: al‧pha‧bet
alphabet (plural alphabets) - The set of letters used when writing in a language.
- The Greek alphabet has only twenty-four letters.
- In the first year of school, pupils are taught to recite the alphabet.
- A writing system in which letters represent phonemes. (Contrast e.g. logography, a writing system in which each character represents a word, and syllabary, in which each character represents a syllable.)
- A true alphabet, a writing system in which there are letters for the consonant and vowel phonemes. (Contrast e.g. abjad.)
- (computer science) A typically finite set of distinguishable symbols.
- Let
 be a regular language over the alphabet be a regular language over the alphabet 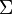 . .
- (India) An individual letter of an alphabet; an alphabetic character.
- 2002, Eugene E. Dike, African myth of creation in African form of writing, Monsenstein und Vannerdat, ISBN 3936600406, page 30:
- We realize the fact that the alphabet A has been used in many world scripts as a vowel with the others AEIOU.
- 2005, Satinder Bal Gupta, Comprehensive Discrete Mathematics & Structures, Laxmi Publications, page 237:
- There are 26 alphabets in English.
- The simplest rudiments; elements.
- Macaulay
- The very alphabet of our law.
[edit] Derived terms [edit] Translations an ordered set of letters used in a language - Afrikaans: alfabet (af)
- Albanian: alfabet (sq)
- Alsatian: Alphabet
- Arabic: حروف الهجاء (ar) (Huruuf al-hijaa') m pl, أبجد (ar) ('ábjad) m, الألفباء (ar) (al-'alifbaa) m, ألفبائية (ar) (al-'alifbaa'iya) f
- Armenian: այբուբեն (hy) (aybuben)
- Asturian: alfabetu (ast) m
- Azeri: əlifba (az)
- Bashkir: әлифба (əlifba)
- Belarusian: алфавіт (be) (alfavít) m, азбука (be) (ázbuka) f
- Bengali: বর্ণমালা (bn) (barṇamālā)
- Bulgarian: азбука (bg) (ázbuka) f
- Burmese: အက္ခရာ (my) (et-hkăya), ခရာ (my) (hkăya)
- Catalan: alfabet (ca) m, abecedari (ca) m
- Chinese:
- Mandarin: 字母 (cmn) (zìmǔ)
- Czech: abeceda (cs) f
- Danish: alfabet (da)
- Dhivehi: އަލިފުބާ (dv)
- Dutch: alfabet (nl)
- Esperanto: alfabeto (eo)
- Estonian: tähestik (et)
- Faroese: stavrað (fo) n
- Filipino: alpabeto
- Finnish: aakkoset (fi) pl, aakkosto (fi)
- French: alphabet (fr) m
- Galician: alfabeto (gl) m
- Georgian: ანბანი (ka) (anbani)
- German: Alphabet (de) n
- Greek: αλφάβητο (el) (alfávito) n
- Ancient: ἀλφάβητος (alphabētos) m
- Hebrew: אלף־בית (he) (alef-bét) m, אלפבית (he) (alpabet) m
- Hindi: वर्णमाला (hi) (varṇamālā) f, मूलाक्षर (hi) (mūlākṣar)
- Hungarian: ábécé (hu)
- Icelandic: stafróf (is) n, rittáknakerfi (is) n
- Ido: alfabeto (io)
- Indonesian: abjad (id), alfabet (id)
- Interlingua: alphabeto (ia)
- Irish: aibítir (ga) f, aibidil (ga) f
- Italian: alfabeto (it) m
- Japanese: アルファベット (ja) (arufabetto), 文字 (ja) (もじ, moji)
- Javanese: aksara (jv), alfabèt (jv)
- Kannada: ಅಕ್ಷರಮಾಲೆ (kn)
- Kazakh: әліпби (kk) (älipbï), әліппе (kk) (älippe)
- Khmer: អក្ខរក្រម (km) (akkʰara krɑm), អក្សរ (km) (aksɑɑ)
- Korean: 알파벳 (ko) (alpabet)
- Lao: ໂຕຫນັງສື (lo), ແມ່ກໍກາ (lo) (mɛ̄ː kɔ̀ː kàː), ອັກສອນ (lo) (ák sɔ̆ːn)
| | - Latin: alphabetum (la) n, abecedārium (la) n
- Latvian: alfabēts (lv)
- Lithuanian: abėcėlė (lt) f, alfabetas (lt) m
- Macedonian: азбука (mk) (ázbuka) f
- Malay:
- Latin: abjad (ms)
- Arabic: ابجد (ms)
- Malayalam: അക്ഷരമാല (ml)
- Maltese: alfabet (mt)
- Marathi: मुळाक्षरे (mr), वर्णमाला (mr)
- Middle Dutch: please add this translation if you can
- Middle English: please add this translation if you can
- Navajo: saad bee álʼíní
- Nepali: please add this translation if you can
- Norwegian: alfabet (no) n
- Old English: stæfrof (ang)
- Old Norse: stafróf
- Persian: الفبا (fa) (alefbâ)
- Polish: alfabet (pl) m, abecadło (pl) n
- Portuguese: alfabeto (pt) m
- Romanian: alfabet (ro) n
- Russian: алфавит (ru) (alfavít) m, азбука (ru) (ázbuka) f
- Sanskrit: अक्षरसमाम्नाय (sa) (akSarasamAmnAya) m
- Scottish Gaelic: aibidil (gd) f
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: азбука (sh) f (Cyrillic alphabet), абецеда (sh) f (Roman alphabet)
- Roman: azbuka (sh) f (Cyrillic alphabet), abeceda (sh) f (Roman alphabet)
- Slovak: abeceda (sk) f
- Slovene: abeceda (sl) f
- Spanish: alfabeto (es) m, abecedario (es) m
- Swedish: alfabet (sv) n
- Tagalog: alpabeto (tl)
- Tajik: алифбо (tg) (ailfbo)
- Tamil: அகரவரிசை (ta) (akaravarisai), நெடுங்கணக்கு (ta) (neṭuṅkaṇakku)
- Tatar: әлифба (tt) (älifba)
- Telugu: అక్షరమాల (te) (aksharamaala)
- Thai: ตัวอักษร (th) (dtua àksŏn), อักษร (th) (àksŏn)
- Turkish: alfabe (tr), abece (tr)
- Turkmen: elipbiý (tk)
- Ukrainian: абетка (uk) (abétka) f, алфавіт (uk) (alfávít) m, азбука (uk) (ázbuka) f, альфабет (uk) (al'fabét) m
- Urdu: حروف تہجی (ur)
- Vietnamese: bảng chữ cái (vi)
- Vilamovian: alfabet n
- Volapük: lafab (vo)
- Võro: tähistü
- West Frisian: alfabet (fy) n
- Yiddish: אלפאבעט (yi) (alfabet) f
|
- The translations below need to be checked and inserted above into the appropriate translation tables, removing any numbers. Numbers do not necessarily match those in definitions. See instructions at Help:How to check translations.
Translations to be checked [edit] See also alphabet (third-person singular simple present alphabets, present participle alphabeting, simple past and past participle alphabeted) - To designate by the letters of the alphabet; to arrange alphabetically.
[edit] External links
[edit] French [edit] Etymology From Late Latin alphabētum, from Ancient Greek ἀλφάβητος (alphabētos), from the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, alpha (Α) and beta (Β), from Phoenician aleph 𐤀 ("ox") and beth 𐤁 ("house"), so called because they were pictograms of those objects. [edit] Pronunciation alphabet m (plural alphabets) - alphabet (set of letters considered as a group)
[edit] Related terms
[edit] Middle French [edit] Etymology From Late Latin alphabētum, from Ancient Greek ἀλφάβητος (alphabētos), from the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, alpha (Α) and beta (Β), from Phoenician aleph 𐤀 ("ox") and beth 𐤁 ("house"), so called because they were pictograms of those objects. alphabet m (plural alphabets) - alphabet (set of letters considered as a group)
 |  |